What Are the Significant Differences Between Building a Conventional Cold Storage and an Advanced Cold Storage?

Advanced cold storage construction, leveraging modern technologies and standard equipment, plays a vital role in extending the shelf life of products. The design and installation of advanced cold storage by specialized teams ensure that refrigeration systems operate with maximum efficiency and minimal energy consumption. Additionally, building advanced cold storage in Tehran, considering the needs of various industries and the city’s climatic conditions, is recognized as a reliable solution for maintaining the cold chain.
Conventional cold storage is typically built based on basic requirements for maintaining low temperatures and usually lacks extensive facilities for precise environmental control. In contrast, constructing advanced cold storage means utilizing modern technology, precise design, and standard equipment that allow full management of storage conditions.
Advanced Cold Storage and Temperature Control
One of the key differences between conventional and advanced cold storage is the precision in controlling temperature and humidity. Conventional cold storage usually has a simple control system that can only adjust within a general temperature range, often resulting in temperature fluctuations.
These fluctuations can reduce food quality or even damage pharmaceuticals. In contrast, advanced cold storage is equipped with digital control systems and smart sensors that provide real-time monitoring of environmental conditions. These systems can detect even the smallest changes in temperature or humidity and automatically adjust them. Such capabilities are critically important in sensitive industries, such as pharmaceuticals and the storage of biological products.
Insulation in the Design and Installation of Advanced Cold Storage
Furthermore, advanced cold storage significantly differs from conventional types in insulation and body design. In simpler cold storage, common insulation materials may be used, which are not very resistant to heat transfer. This results in higher energy consumption and reduced system efficiency.
Advanced cold storage, however, uses modern insulation with greater thickness and quality, minimizing heat transfer and saving a significant amount of energy. This also reduces long-term operational costs, making investment in advanced cold storage highly cost-effective.
Advanced Cold Storage in Tehran and the Equipment Used
Another difference concerns main equipment such as compressors, evaporators, and condensers. Conventional cold storage often uses standard equipment with medium capacity that can only meet basic requirements. These systems are vulnerable to high operating pressures or long-term use and require frequent maintenance.
Advanced cold storage, on the other hand, utilizes high-efficiency compressors, multi-stage evaporators, and low-energy condensers that not only have longer lifespans but also deliver optimal performance. This equipment performs efficiently under various climatic conditions, especially in large cities like Tehran, where temperature fluctuations are significant.
Intelligent systems are another feature of advanced cold storage. In conventional systems, operators must perform many tasks manually, increasing the likelihood of errors. In advanced cold storage, smart systems allow integrated management. For example, managers can monitor the real-time status of the cold storage through mobile applications or web-based systems and issue necessary commands remotely. This capability not only increases efficiency but also enhances safety and reliability for industrial owners.
Energy consumption and environmental impact are also fundamental distinctions between conventional and advanced cold storage. Conventional cold storage typically uses refrigerants that may harm the environment or fail to meet international standards. Advanced cold storage uses eco-friendly refrigerants and energy-efficient systems, helping reduce energy costs and supporting environmental sustainability. This is especially important for companies that prioritize social responsibility.
In conclusion, constructing advanced cold storage is fundamentally different from conventional cold storage, and these differences are evident in all aspects, from design and equipment to operation and energy consumption.
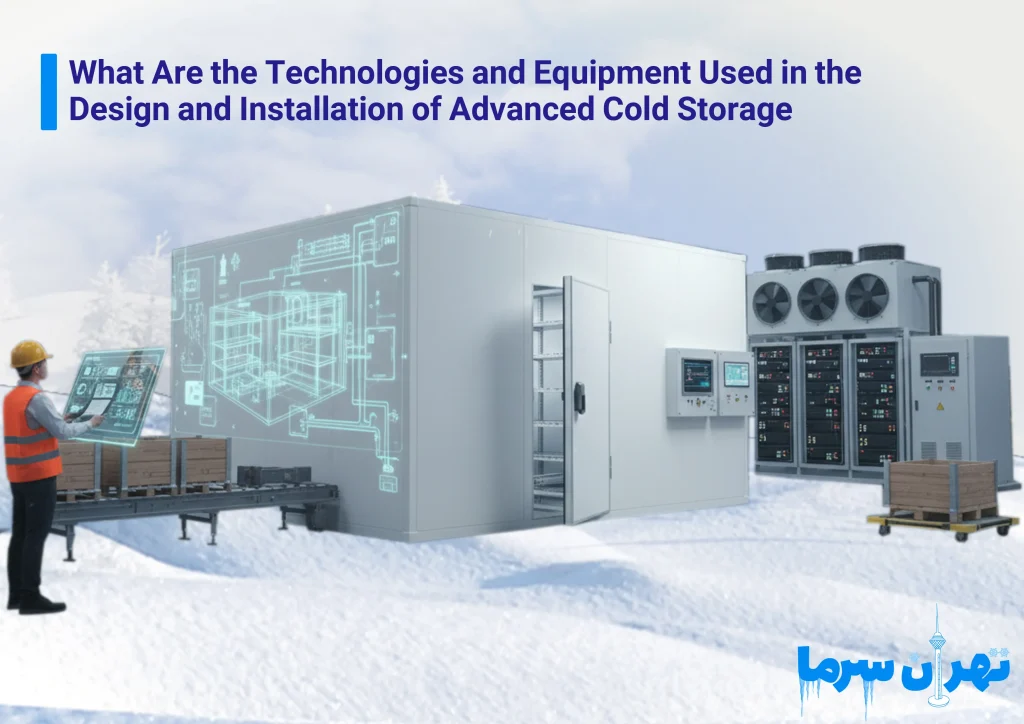
What Are the Technologies and Equipment Used in the Design and Installation of Advanced Cold Storage
One of the most critical pieces of equipment in advanced cold storage design is the compressor. The compressor is essentially the heart of the refrigeration system, responsible for compressing the refrigerant and initiating the cooling cycle. In conventional cold storage, compressors usually operate at a fixed capacity, which leads to higher energy consumption and increased wear.
In advanced cold storage, inverter and multi-stage compressors are used, which can adjust capacity according to real-time demand. This significantly reduces energy consumption, reduces stress on components, and extends the system’s lifespan.
Next are the evaporator and condenser, which together play a decisive role in system performance. Evaporators in advanced cold storage are designed to ensure uniform cooling throughout the storage area. These units are typically equipped with energy-efficient and high-powered fans that optimize cold air circulation. Condensers are also optimized and energy-efficient, often designed with copper pipes and aluminum fins to improve heat transfer efficiency. Many modern projects utilize air-cooled or water-cooled condensers with new technologies, which increase efficiency while reducing water and energy consumption.
Another critical factor in advanced cold storage is insulation and the choice of materials. Although insulation may seem like a minor detail, it significantly impacts energy consumption and internal temperature stability. Advanced cold storage uses high-density sandwich panels that prevent heat transfer between the interior and exterior. These panels not only prevent energy loss but also offer high resistance to moisture and mechanical pressure, significantly extending the facility’s lifespan.
Smart control systems are also central to modern cold storage. These systems, equipped with precise temperature and humidity sensors, monitor environmental conditions in real-time. The collected data is processed by a central unit, which makes necessary adjustments to compressor or fan operations. Importantly, these systems also allow remote management, enabling managers to monitor the facility and receive alerts via mobile or computer even when off-site. This level of automation reduces human error and significantly improves product safety.
Additionally, using environmentally friendly refrigerants is a major consideration. Older refrigerants consumed more energy and damaged the ozone layer, but modern alternatives are low-impact and meet global standards, maintaining efficiency while minimizing environmental harm. This aligns with global sustainability goals and enhances the economic and social value of investing in advanced cold storage.
Energy optimization systems are another key technology in modern cold storage. By combining intelligent algorithms with energy-efficient equipment, these systems reduce electricity consumption during peak hours while maintaining stable cooling. Some systems can generate and store extra cooling during off-peak hours and reduce electrical load during peak periods. This intelligent energy management lowers costs, stabilizes the power grid, and prevents extreme fluctuations.
Overall, the design and installation of advanced cold storage rely on a suite of modern technologies and specialized equipment aimed at increasing efficiency, reducing operational costs, enhancing safety, and preserving product quality.
Engineering Design and Technical Calculations in Building Advanced Cold Storage
Engineering design and technical calculations in advanced cold storage construction are among the most critical stages, determining the final quality, system efficiency, and equipment lifespan. A cold storage facility is not merely an enclosed space for low temperatures; it is a complex system comprising mechanical, electrical, and structural components that must be designed and executed according to precise engineering principles.
If this process is not carried out correctly, even the best equipment cannot perform optimally. Therefore, engineering design in advanced cold storage is vital and indispensable.
One of the first steps in engineering design is calculating the cooling load. The cooling load represents the amount of cooling required to maintain stable temperatures in the cold storage, and it is calculated based on factors such as the type of product, storage volume, product inflow and outflow, climatic conditions, and storage duration.
In advanced cold storage, these calculations are performed using precise engineering software to avoid even the smallest errors in equipment capacity selection. The choice of compressor, condenser, and evaporator all depend on these calculations, and any mistake can lead to higher energy consumption or internal temperature instability.
Insulation is another key aspect of technical design in advanced cold storage, playing a critical role in reducing the cooling load. At this stage, engineers must determine the appropriate type and thickness of insulation based on climate conditions and the cold storage application. For example, in hot climates, thicker and more resistant insulation is needed to prevent heat infiltration.
Using high-density sandwich panels in advanced cold storage design is considered one of the best solutions, reducing energy loss while increasing structural strength.
Designing the ventilation and air circulation system is also an essential part of technical calculations. Different products require varying cooling distribution. In conventional cold storage, temperature inconsistencies are often observed across different areas, which can affect product quality.
However, in advanced cold storage engineering design, evaporator placement and precise airflow calculations are carried out to ensure uniform temperature throughout the facility. This is critically important for products such as pharmaceuticals or protein-based goods.
Additionally, designing control systems is an integral part of the engineering process. Modern systems are equipped with precise temperature and humidity sensors that continuously record and analyze data. These systems can automatically adjust equipment operation or issue alerts in case of any malfunction. Software design and algorithmic calculations in this area ensure stable long-term cold storage performance.
Another crucial aspect of advanced cold storage engineering is energy optimization. Engineers must accurately calculate and select equipment capacities to meet cooling needs while minimizing electricity consumption. The use of inverter compressors, energy-efficient fans, and energy recovery systems are among the solutions prioritized in advanced designs.
Installation and Implementation Stages in Building Advanced Cold Storage
Installation and implementation of advanced cold storage is a multi-step, precise process that must comply with engineering principles and international standards to ensure optimal system performance. This process typically begins with site preparation and substructure work, where the proper foundation for the cold storage is established, and considerations such as ground load-bearing capacity, floor insulation, and substructure for insulation panels are addressed.
Next, sandwich panels are installed as walls, ceilings, and floors to create an insulated environment resistant to thermal exchange. The main equipment—including compressors, condensers, evaporators, and refrigerant piping systems—is then installed and interconnected according to initial design and technical calculations. Proper installation of electrical systems, control panels, and smart sensors is also essential, as stable operation and intelligent management depend on these components.
After installation, initial testing and commissioning are conducted to verify refrigerant pressure, temperature, humidity, and overall functionality. Finally, the cold storage is handed over, and operator training is provided. With regular maintenance and proper servicing, long-term performance is ensured.
Energy Optimization and Extending Equipment Lifespan in Advanced Cold Storage
Energy optimization and extending the lifespan of equipment are among the primary objectives considered throughout the design and implementation of advanced cold storage. The use of inverter compressors and energy-efficient equipment minimizes electricity consumption and reduces stress on components.
Precise insulation with standard sandwich panels prevents heat loss and maintains stable temperature conditions, reducing energy costs and equipment wear. Engineering design of ventilation systems and strategic evaporator placement ensures uniform cooling distribution and prevents overworking compressors.
Furthermore, the use of smart temperature and humidity control systems enables real-time monitoring of cold storage performance. Any disruption triggers automatic adjustments, preventing serious damage and extending equipment lifespan.
Using environmentally friendly refrigerants and energy recovery systems also significantly reduces consumption and improves efficiency. Consequently, these measures ensure that advanced cold storage is not only energy-efficient but also highly durable, making the initial investment economically viable in the long term.
Building Advanced Cold Storage with Tehran Sarma Engineering Company
Constructing advanced cold storage with Tehran Sarma Engineering Company offers a professional and comprehensive experience, covering all stages of design, installation, and commissioning according to the highest engineering standards. By leveraging specialized teams and modern equipment, the company can design and implement high-efficiency cold storage facilities with precise temperature and humidity control, ensuring optimal storage conditions for various products, including food, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural goods.
Throughout the construction process, all technical calculations—including cooling load, equipment placement, and precise insulation—are conducted to ensure system efficiency, minimal energy consumption, and extended equipment lifespan. Tehran Sarma also employs smart monitoring and control technologies, enabling remote management and rapid response to any changes in conditions, ensuring product safety and quality.
The use of eco-friendly refrigerants and energy optimization systems further reduces operational costs and demonstrates compliance with environmental standards.
By choosing Tehran Sarma, customers can be confident that their investment in advanced cold storage will meet current needs while ensuring long-term sustainability and efficiency. Professional post-installation support and technical maintenance provide added value to this investment.
For more information on cold storage construction costs, visit Tehran Sarma’s website or contact 09201906418.
In conclusion, building advanced cold storage is now essential for the food, pharmaceutical, and agricultural industries. Proper engineering design and installation according to international standards guarantee accurate and stable system performance. In Tehran, constructing advanced cold storage holds a special position due to the concentration of industries and extensive market demand, contributing significantly to supply chain development and support.
Source:
https://www.coldstorageus.com/



 سردخانه
سردخانه برق
برق کمپرسور
کمپرسور کمپرسور بیتزر
کمپرسور بیتزر کمپرسور کوپلند
کمپرسور کوپلند کمپرسور بوک
کمپرسور بوک کمپرسور دانفوس
کمپرسور دانفوس کمپرسور منیروپ دانفوس
کمپرسور منیروپ دانفوس کمپرسور امبراکو
کمپرسور امبراکو کمپرسور پاناسونیک
کمپرسور پاناسونیک کمپرسور سابکول
کمپرسور سابکول کمپرسور کوپلند
کمپرسور کوپلند کمپرسور اسکرال کوپلند
کمپرسور اسکرال کوپلند کمپرسورفراسکلد
کمپرسورفراسکلد کمپرسور رفکامپ
کمپرسور رفکامپ کمپرسور اسکرال دانفوس
کمپرسور اسکرال دانفوس گاز مبرد
گاز مبرد گاز R22
گاز R22 گاز R134
گاز R134 گاز R404
گاز R404 گاز R407
گاز R407 گاز R410
گاز R410 گاز R508
گاز R508 کندانسور هوایی
کندانسور هوایی اواپراتور
اواپراتور اواپراتور آرشه
اواپراتور آرشه اواپراتور صابکول
اواپراتور صابکول اواپراتور آسه
اواپراتور آسه اواپراتور نیک
اواپراتور نیک اواپراتور آرتک
اواپراتور آرتک اواپراتور نوین
اواپراتور نوین اواپراتور تبادل کار
اواپراتور تبادل کار درب
درب ساندویچ پنل
ساندویچ پنل فن سردخانه
فن سردخانه روغن کمپرسور سانیسو
روغن کمپرسور سانیسو متعلقات سردخانه
متعلقات سردخانه